Nurture your body and mind by cultivating a healthy relationship with food using our expert advice.
Cultivating a healthy relationship with food is an essential component of maintaining overall physical, mental, and emotional well-being.
The relationship we have with food can be positive or negative, depending on our attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors surrounding eating and nutrition.
A healthy relationship with food involves nourishing our bodies with wholesome and balanced meals, being mindful of our eating patterns, and avoiding restrictive or binge eating habits.
It is important to recognize that our relationship with food is shaped by various factors such as genetics, upbringing, and societal norms.
However, regardless of our background and circumstances, we can take steps to develop a positive and healthy relationship with food.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the Importance of Nutritious Foods in Your Diet
Nutritious foods are essential for maintaining optimal health, promoting energy levels, and preventing chronic diseases.
Nutritious foods contain the necessary nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, fiber, and healthy fats, that our bodies need to function properly.
Eating a diet rich in nutritious foods can help to reduce inflammation in the body, boost our immune system, and even protect against certain types of cancer.
Some of the key benefits of including nutritious foods in your diet include improved digestion, better weight management, reduced risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease, and improved cognitive function.
Additionally, consuming nutrient-dense foods can help to improve mood, increase energy levels, and enhance overall feelings of well-being.
How to Pay Attention to Your Body’s Hunger Signals
Mindful eating is a practice that involves paying attention to your body’s hunger signals and eating with intention and awareness.
This approach to eating can help to promote healthier eating habits, improve digestion, and reduce overeating and emotional eating.
To practice mindful eating, start by paying attention to your body’s physical sensations of hunger and satiety.
Eat when you feel hungry, and stop eating when you feel satisfied, even if you haven’t finished everything on your plate.
Aim to eat slowly, savoring the flavors and textures of your food, and take breaks to check in with your body and assess your level of hunger.
It can also be helpful to eliminate or reduce distractions while eating, such as watching TV or scrolling through social media.
Instead, focus your attention on your food and the sensations you experience while eating. Pay attention to how your body feels before, during, and after eating, and use this information to make informed choices about what and how much you eat.
By practicing mindful eating, you can learn to develop a healthier relationship with food, tune into your body’s natural hunger and satiety cues, and promote more balanced, healthy eating habits.
Avoiding Fad Diets and Choosing a Sustainable Healthy Eating Plan
Fad diets are temporary diets that often promise quick weight loss results through strict rules or extreme restrictions.
However, they often lack essential nutrients and may be too restrictive to follow in the long term, which can lead to unhealthy eating habits, nutrient deficiencies, and even weight gain when returning to regular eating patterns.
Instead of focusing on fad diets, it is essential to choose a sustainable, healthy eating plan that you can maintain for the long term while aligning with your lifestyle and health goals.
Choosing a sustainable healthy eating plan involves finding a balanced approach that promotes eating a variety of nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
It should also be flexible and adaptable to allow for occasional indulgences or changes in dietary preferences or needs.
To choose a sustainable healthy eating plan, try focusing on whole, minimally processed foods and lean protein sources.
Add in plenty of fruits and vegetables, and limit saturated and trans fats, added sugar, and salt.
Avoid labeling food as “good” or “bad” and instead strive for moderation, balance, and variety in your diet.
Additionally, consider speaking with a registered dietitian or nutritionist to develop a personalized plan that aligns with your specific needs and goals.
Strategies for Overcoming Emotional Eating Habits
Emotional eating is a common coping mechanism that involves eating as a response to negative or stressful emotions such as anxiety, loneliness, boredom, or sadness.
While it may provide comfort in the short term, it can lead to guilt, shame, or regret, and eventually lead to an unhealthy relationship with food and unwanted weight gain.
Here are some effective strategies for overcoming emotional eating habits:
Identify triggers
Try to identify the emotions or situations that trigger emotional eating, such as stress at work or relationship issues.
Once identified, develop alternative coping strategies for these triggers, such as talking to a friend or engaging in a relaxing activity like yoga or meditation.
Practice mindfulness
Pay attention to your body’s physical hunger cues and eat mindfully, slowly savoring the flavors and textures of food.
This helps you focus on the experience of eating, appreciate your food, and helps to reduce emotional eating behaviors.
Keep a food journal
Keeping a food journal can help you identify patterns in your eating behaviors to distinguish between hunger and emotions, enabling you to adjust and change your relationship with food.
Create a supportive environment
Create a positive and supportive environment by surrounding yourself with people who focus on self-care and encourage healthy eating practices by providing healthy food options and tone-setting a positive outlook towards food and eating.
Seek professional help
If emotional eating is overwhelming and persistent, consider seeking professional help, like a registered dietitian, a psychotherapist, or a counselor.
Making Healthy Eating Fun and Enjoyable
Healthy eating does not have to be monotonous or boring; seamlessly integrating fun and enjoyment into your healthy eating habits can help sustain your diet in the long term.
Here are some strategies you can use to make healthy eating fun and enjoyable:
Experiment with new recipes
Try out new recipes that incorporate healthy and diverse ingredients to add variety to your meals while discovering new delicious ingredients and spices.
Customize your meals
Encourage creativity and artistic flair when composing meals, making them visually appetizing as well as nutritious.
Opt for a brightly colored, Instagram-worthy food grade on your plate or bowls, and let your creative side run free!
Engage in social eating
Make meal times a social experience by inviting friends or family over for healthy meal preparation and sharing.
This creates a sense of accountability and enjoyment when everyone shares the responsibility of cooking and eating together.
Make healthy treats
Prepare and indulge in healthy treats such as smoothie bowls made with fruits and veggies, low-calorie fruit ice cream, or baked kale chips.
Mix and match your meals
Mix and match different protein sources, and vegetables to create delicious and diverse meals.
Customize your meals to fit your taste buds by creating different combinations of spices and herbs to add excitement to your meals.
Simple Tips for Healthy Cooking and Meal Preparation
Preparing healthy meals at home is an essential component of maintaining a healthy diet, and with some simple tips, cooking, and meal preparation can become a fun and easy experience. Here are some simple tips for healthy cooking and meal preparation:
- Plan ahead: Plan your meals for the week, taking into consideration your daily schedule and lifestyle. Preparing a weekly grocery list and purchasing only what you need will save time and can promote financial management.
- Keep healthy staples stocked: Always have some basic, healthy foods such as brown rice, whole-grain pasta, canned beans, canned vegetables, frozen fruits and vegetables, and lean protein options such as chicken breast or fish in your pantry and freezer for convenient meal preparation.
- Use healthy cooking methods: Favor healthy cooking methods like grilling, steaming, baking or roasting instead of frying or deep frying to eliminate excess calories and unnecessary fat.
- Add flavor without too much salt, sugar, or fat: Utilize natural spices and herbs to enhance flavor without adding extra calories, salt, or unhealthy fats.
- Make food in batches: Prepare larger quantities of food than you need and store the leftovers in the freezer for future meals. This not only saves time but can also help prevent the temptation of ordering out or eating unhealthy takeout food.
- Choose healthy snacks: Snack on healthy foods such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, as well as low-fat yogurts and hummus to keep your energy levels up throughout the day.
The Benefits of Regular Physical Activity in Maintaining a Healthy Relationship with Food
Regular physical activity plays an essential role in creating and maintaining a healthy relationship with food.
Exercise not only helps to burn calories and support weight management but can also improve our mental and emotional well-being, which can help reduce emotional eating and improve our overall relationship with food.
Here are some of the specific benefits of regular physical activity in maintaining a healthy relationship with food:
- Increases awareness of hunger and satiety: Regular exercise increases awareness of hunger and satiety cues. This awareness can help to reduce overeating and bingeing behaviors while promoting a more balanced and intentional approach to eating.
- Reduces stress and anxiety: Exercise has been shown to reduce stress and anxiety, which can help prevent emotional eating and minimize the impact of stress on our dietary patterns and choices.
- Improves mood and self-esteem: Regular physical activity promotes the release of endorphins, enhancing mood and self-esteem, which can reduce the likelihood of turning to food as a source of comfort or emotional management.
- Supports digestive health: Exercise has been associated with improving digestive health and promoting proper bowel movements, which can improve nutrient absorption and have positive effects on overall physical health.
- Provides the opportunity for social interaction: Participating in group exercise classes or sports activities can provide opportunities for social interaction, which can reduce feelings of isolation or loneliness, help improve mood, and foster a sense of accountability towards healthy lifestyle habits.
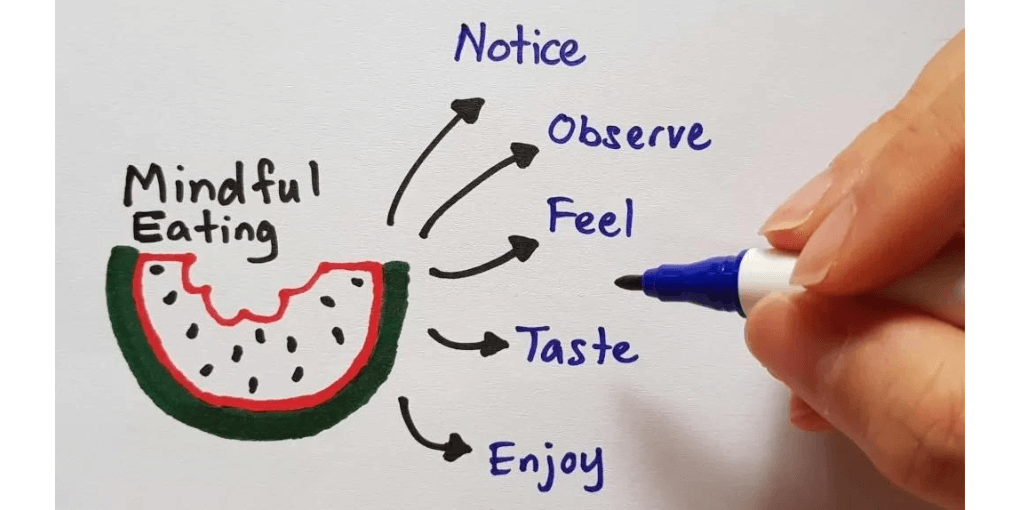
Mindful Eating: Listening to Your Body
Mindful eating is a practice that involves paying full attention to the experience of eating and listening to your body’s cues and signals.
It’s about being present in the moment and cultivating a deeper appreciation for food. Here are some tips for practicing mindful eating:
- Eat slowly: Take your time to chew and savor each bite. Eating slowly allows you to fully experience the taste, texture, and aroma of your food. It also gives your body a chance to recognize when it is full.
- Avoid distractions: Minimize external distractions such as television, smartphones, or work while eating. Focus on the act of eating and give it your full attention.
- Tune in to your hunger and fullness cues: Before you start eating, check in with your body to gauge your hunger levels. During the meal, pause occasionally to assess your fullness. Listen to your body’s signals and eat until you are comfortably satisfied, rather than eating until you feel stuffed.
- Be aware of your senses: Pay attention to how your food looks, smells, and tastes. Take pleasure in the experience of eating and appreciate the nourishment it provides.
- Practice gratitude: Take a moment to be thankful for your food. Reflect on where it came from, how it was prepared, and the effort that went into providing it.
- Notice emotional eating triggers: Sometimes we turn to food for comfort or as a distraction. Become aware of your emotional triggers and practice finding alternative ways to address those emotions, such as journaling, walking, or talking to a friend.
- Enjoy the process: Mindful eating is about more than just the food itself. Enjoy the process of meal preparation, cooking, and choosing ingredients. Engage all your senses, from selecting fresh produce to savoring the aroma of a delicious meal.
Emotional Eating and Its Impact
Emotional eating is the practice of eating to cope with or soothe emotions rather than to satisfy physical hunger.
While emotional eating is a normal aspect of life, relying on food to regulate emotions can have a number of harmful consequences:
Weight gain
Emotional eating often involves indulging in high-calorie, comfort foods, which can lead to weight gain over time.
Consuming excessive calories without a genuine physical hunger can result in an imbalance between energy intake and expenditure.
Poor nutrition
Emotional eating tends to involve unhealthy, processed foods that are high in sugar, fat, and salt.
Relying on these types of foods can lead to a poor overall diet lacking in essential nutrients, which can negatively impact physical health.
Cycle of emotional dependency
Turning to food for emotional consolation can lead to a vicious cycle in which food becomes the major coping method for dealing with emotions.
This can hinder the development of healthy emotional regulation skills and other effective coping strategies.
Decreased self-esteem
Emotional eating can negatively affect self-esteem and body image. The feelings of guilt, shame, or dissatisfaction with one’s eating habits can further contribute to a negative self-perception.
Meal Planning for Success
Meal planning is a helpful technique to set yourself up for success when it comes to eating healthy, saving time, and reducing stress. Here are some tips for effective meal planning:
Set a schedule
Set aside time each week to plan your meals. This might be on a weekend or any other day that is convenient for you. Consistency is key to staying organized and prepared.
Take inventory
Before planning your meals, take stock of what you already have in your pantry, refrigerator, and freezer. This will help you build your meals around ingredients you already have on hand, reducing waste and saving money.
Plan balanced meals
Aim for a good balance of protein, carbohydrates, healthy fats, and vegetables or fruits in each meal.
Consider incorporating a variety of colors, textures, and flavors to make your meals more interesting and nutritious.
Consider your schedule
Take into account your daily activities and obligations when planning your meals. Choose simple and quick recipes for busy days and prep more elaborate dishes when have more time available.
Batch cooking
Prepare larger quantities of certain dishes that can be used for multiple meals throughout the week.
This can include grains, proteins, or roasted vegetables that can be used as building blocks for different meals.
Shop with a list
Once you have your meal plan, create a shopping list to ensure you have all the necessary ingredients on hand. Stick to your list to avoid impulse purchases and stay focused on your goals.
Prep in advance
Take some time to chop vegetables, marinate proteins, or pre-cook certain components of your meals in advance.
This can significantly reduce cooking time and make meal preparation during the week more efficient.
Food and Mental Health
The food we consume plays a significant role in our overall physical and mental well-being. Several studies have shown connection between diet and mental. Here are some ways which food can impact mental health.
Nutrient deficiencies A diet lacking in essential nutrients can contribute to mental issues. Certain nutrients, such as omega3 fatty acids, B vitamins, vitamin, and magnesium, have been linked to brain health and the prevention or management of conditions like depression and anxiety.
Gut-brain connection
The gut-brain axis is the link between the gut and the brain. The balance of bacteria in the gut, known as the gut microbiome, can influence mental health.
A healthy gut microbiome, supported by a diet rich in fiber, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods, may positively impact mood and cognition.
Blood sugar regulation
The consumption of highly processed and sugary foods can cause blood sugar spikes and crashes, leading to mood swings, fatigue, and irritability.
Balancing blood sugar levels through a diet that includes complex carbohydrates, fiber, protein, and healthy fats can help stabilize mood and energy levels.
Inflammation
Chronic inflammation has been linked to various mental health conditions, including depression and anxiety. The foods we eat can either promote or reduce inflammation in the body.
Foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, can help combat inflammation.
Impact of food on neurotransmitters
Certain nutrients can influence the production and functioning of neurotransmitters in the brain, which play a crucial role in regulating mood and emotions.
For instance, foods rich in tryptophan, an amino acid, can promote the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with feelings of well-being.
Kitchen Essentials for a Healthy Diet
Having the right kitchen essentials can make it easier and more convenient to maintain a healthy diet. Here are some kitchen items that can support your efforts to eat nutritiously:
- Cutting board and knives: Invest in a durable cutting board and a set of good-quality knives for slicing and chopping fruits, vegetables, and other ingredients. They make meal preparation quicker and more efficient.
- Blender or food processor: These appliances are versatile tools for creating smoothies, purees, sauces, and homemade dressings. They can also be used for blending ingredients for soups and stews.
- Measuring cups and spoons: Accurate portioning is important when following recipes or tracking your food intake. Having a set of measuring cups and spoons allows you to measure ingredients precisely.
- Non-stick skillet or frying pan: A non-stick skillet or frying pan can reduce the need for excessive cooking oil or butter when preparing meals. It can be used for sautéing vegetables, making omelets, and cooking lean proteins.
- Baking sheet and oven-safe dish: Baking sheets are ideal for roasting vegetables, making baked chicken, or preparing homemade granola. An oven-safe dish is great for casseroles or baking recipes.
The Role of Exercise and Lifestyle Choices
Exercise and lifestyle choices play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being, including mental health. Here are some ways exercise and lifestyle choices can benefit you:
- Physical health: Regular exercise contributes to maintaining a healthy weight, reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. It promotes cardiovascular health, bone and muscular strength, and general physical fitness.
- Stress reduction: Engaging in regular exercise or physical activity can help reduce stress levels. Exercise triggers the release of neurochemicals like endorphins, dopamine, and serotonin, which can have a positive impact on stress management and overall mood.
- Cognitive function: Physical activity has been linked to improved cognitive function, memory, and concentration. Exercise increases blood flow to the brain, promoting the growth of new cells and enhancing brain health.
Energy and productivity: Regular exercise can help increase energy levels and improve productivity. It boosts circulation, delivering oxygen and nutrients throughout the body, leading to increased alertness, focus, and overall productivity.
Conclusion
Maintaining a healthy relationship with food involves prioritizing nutrient-rich foods, practicing mindful eating, avoiding fad diets, and incorporating enjoyable physical activities.
Strategies such as experimenting with new recipes, keeping healthy staples stocked, and engaging in social eating can make healthy cooking and meal preparation fun and enjoyable.
Additionally, adopting stress-reducing techniques, practicing good sleep hygiene, and creating a positive environment can help mitigate the impact of sleep and stress on our eating habits and support overall well-being.
By implementing these strategies, we can foster a more positive outlook toward food and cultivate positive lifestyle habits over time.




