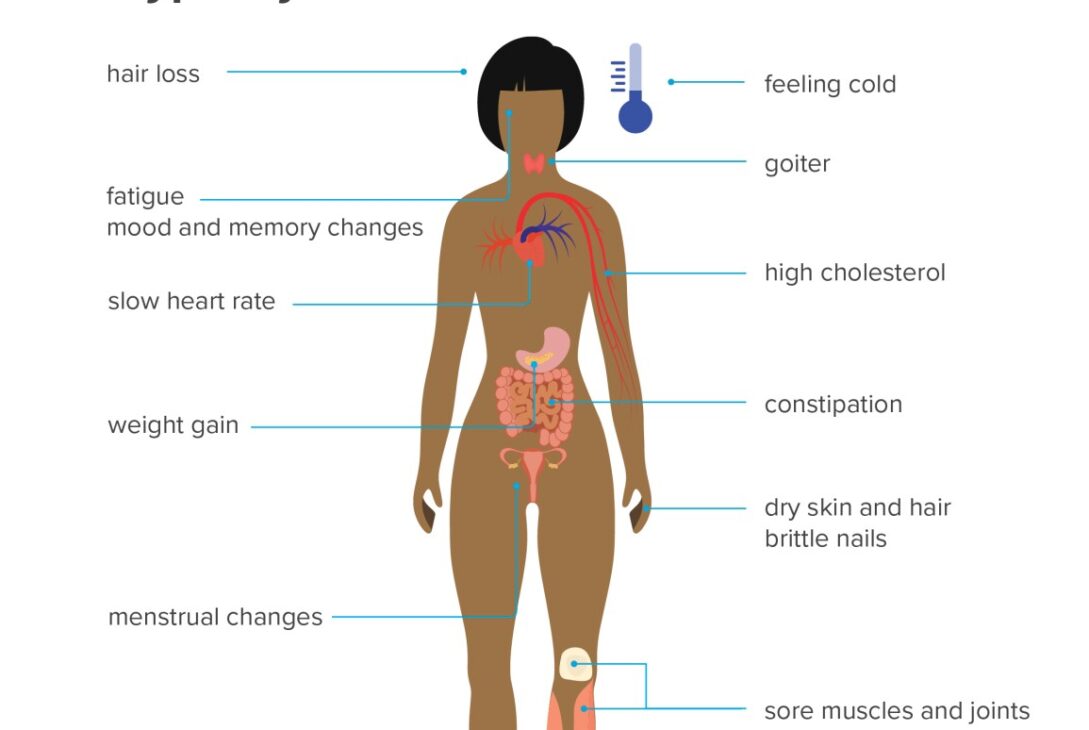
Weight gain due to thyroid issues often includes symptoms like fatigue, cold intolerance, and dry skin. Blood tests can confirm thyroid function.
Thyroid-related weight gain is commonly linked to hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland produces insufficient hormones. This affects metabolism, causing symptoms such as fatigue, cold intolerance, and dry skin. The thyroid gland plays a critical role in regulating metabolism, and its dysfunction can lead to unexplained weight gain.
If you experience these symptoms, consult a healthcare provider. Blood tests can help diagnose thyroid issues. Early detection and treatment can manage symptoms effectively. Understanding the signs and seeking medical advice are essential steps for proper diagnosis and treatment. Keep track of your symptoms and consult a professional for accurate diagnosis.

Credit: www.everydayhealth.com
Thyroid Function And Weight
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck. It plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions. One of its primary roles is controlling metabolism. This, in turn, affects how your body uses energy. A disrupted thyroid function can lead to weight gain or weight loss. Understanding this relationship is key to managing your health.
Thyroid Hormones
The thyroid produces two main hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones regulate the body’s metabolic rate. They influence how fast or slow your body burns calories. When the thyroid doesn’t produce enough T3 and T4, it’s called hypothyroidism. This condition often leads to weight gain.
Conversely, too much T3 and T4 can cause hyperthyroidism. This condition can result in weight loss. Both conditions impact your body’s energy balance. Understanding these hormones helps in identifying the root cause of weight changes.
Metabolism Impact
Metabolism refers to all the chemical processes that occur within the body. Thyroid hormones have a significant impact on metabolism. They determine how quickly the body converts food into energy.
| Thyroid Condition | Metabolic Rate | Weight Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Hypothyroidism | Slowed | Weight Gain |
| Hyperthyroidism | Increased | Weight Loss |
For those with hypothyroidism, the body burns calories slower. This leads to weight gain, even with a normal diet. For hyperthyroidism, the body burns calories faster. This can result in weight loss, despite increased food intake.
Monitoring thyroid function is essential for maintaining a healthy weight. If you experience unexplained weight changes, consider checking your thyroid levels.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/hypothyroidism-leptin-rt3-weight-gain-3233049_final-4be61734de17488db0529704545f6b98.jpg)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
Common Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders can impact your weight. Understanding these disorders helps in managing your health better. Below, we explore two common thyroid disorders.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough hormones. This can slow down your metabolism, causing weight gain. Common symptoms of hypothyroidism include:
- Fatigue
- Cold intolerance
- Dry skin
- Constipation
A blood test can diagnose hypothyroidism. Treatment often involves taking synthetic thyroid hormones.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is when the thyroid gland produces too many hormones. This speeds up your metabolism, sometimes causing weight loss. Common symptoms of hyperthyroidism include:
- Increased appetite
- Heat intolerance
- Palpitations
- Weight loss
A blood test can diagnose hyperthyroidism. Treatment options may include medications, radioactive iodine, or surgery.
| Disorder | Symptoms | Diagnosis | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothyroidism | Fatigue, Cold intolerance, Dry skin, Constipation | Blood test | Synthetic thyroid hormones |
| Hyperthyroidism | Increased appetite, Heat intolerance, Palpitations, Weight loss | Blood test | Medications, Radioactive iodine, Surgery |
Symptoms Of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism, or an underactive thyroid, can affect your body’s metabolism. This condition often leads to several symptoms that can disrupt daily life. Understanding these symptoms can help identify if weight gain is due to thyroid issues.
Weight Gain
One of the most noticeable symptoms of hypothyroidism is unexplained weight gain. The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism. When the thyroid is underactive, your metabolism slows down. This can result in weight gain, even with no change in diet or exercise.
Look for a gradual increase in weight over time. If you notice this, it might be due to hypothyroidism. The weight gain is usually moderate but can become significant without treatment.
Fatigue
Fatigue is another common symptom of hypothyroidism. Feeling tired and sluggish is typical when the thyroid hormone levels are low. This lack of energy can affect daily tasks and overall quality of life.
Many people with hypothyroidism report feeling exhausted even after a full night’s sleep. If you feel unusually tired, it may be worth discussing thyroid testing with your doctor.
Dry Skin
Dry skin can also be a symptom of hypothyroidism. Thyroid hormones help regulate skin moisture. Without enough of these hormones, your skin may become dry and rough.
You might notice flaky skin or cracks, especially on your hands and feet. This symptom can be uncomfortable and might worsen over time.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Weight Gain | Unexplained increase in weight due to slow metabolism. |
| Fatigue | Persistent tiredness and low energy levels. |
| Dry Skin | Rough, flaky skin due to reduced moisture. |
Diagnosing Thyroid Issues
Weight gain can be frustrating. Sometimes, it may be due to thyroid problems. Diagnosing thyroid issues early is essential. This helps in managing weight and overall health. Below are key methods for diagnosing thyroid issues.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are crucial for diagnosing thyroid problems. The most common test is the TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) test. High TSH levels often indicate an underactive thyroid or hypothyroidism. Low TSH levels may suggest an overactive thyroid or hyperthyroidism.
Other blood tests include:
- Free T4 – Measures the amount of active thyroid hormone.
- Free T3 – Measures the levels of another active thyroid hormone.
- Thyroid Antibodies – Helps detect autoimmune thyroid conditions.
Doctors analyze these results to diagnose thyroid issues accurately.
Physical Examination
A physical examination helps in diagnosing thyroid issues. Doctors check for signs like:
- Swelling in the neck area.
- Dry skin or brittle hair.
- Changes in heart rate.
Doctors may also feel the thyroid gland during the exam. This helps identify any abnormalities or lumps. Combining physical examination with blood tests offers a comprehensive diagnosis.
Understanding these methods can help you take control of your health. Early detection and treatment can make a significant difference.
Thyroid Vs. Lifestyle Factors
Gaining weight can be frustrating. Understanding the root cause is essential. Sometimes it’s linked to thyroid problems. Other times, lifestyle factors play a role. Let’s explore how to tell the difference.
Diet And Exercise
A balanced diet and regular exercise are crucial. If you eat unhealthy foods, you may gain weight. The same goes for a sedentary lifestyle.
- High-calorie intake: Eating more calories than you burn leads to weight gain.
- Lack of physical activity: Not exercising can cause weight increase.
Keeping a food diary can help you track your eating habits. This can show if your diet is causing weight gain. If you exercise regularly and still gain weight, it might be your thyroid.
Stress Levels
Stress affects your body in many ways. High stress can lead to weight gain.
| Factor | Effect on Weight |
|---|---|
| Stress Hormones | Increased cortisol levels can cause weight gain. |
| Emotional Eating | Stress can lead to overeating. |
Managing stress is important for overall health. Practices like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help. If stress reduction doesn’t help with weight loss, thyroid issues might be the cause.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/seven-thyroid-diet-secrets-3233060_color3-5b6c602ec9e77c005046101a-6103f6f07d884baf9088b5b7936d6b2a.png)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
Treatment Options
Understanding weight gain due to thyroid issues can be overwhelming. Fortunately, there are effective treatment options. These options can help you manage your weight and improve your health. Below are some key treatments to consider.
Medication
Medication is a common treatment for thyroid-related weight gain. Thyroid hormone replacement therapy is often prescribed for hypothyroidism. This therapy involves taking synthetic hormones to balance your thyroid levels.
A common medication is Levothyroxine. It helps restore normal thyroid function. Your doctor will adjust the dosage based on your thyroid levels. Regular blood tests ensure the medication is working effectively.
Sometimes, other medications may be needed. These can include drugs to manage symptoms like fatigue and depression. Always consult your doctor before starting any new medication.
Dietary Changes
Dietary changes can significantly impact thyroid health and weight. Focus on a balanced diet rich in nutrients. Avoid foods that can interfere with thyroid function.
| Food Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Goitrogenic Foods (Limit) | Soy, broccoli, cauliflower |
| Iodine-Rich Foods | Seaweed, fish, dairy |
| Anti-inflammatory Foods | Turmeric, berries, leafy greens |
Include selenium and zinc in your diet. These minerals support thyroid function. Foods like nuts, seeds, and legumes are good sources.
Stay hydrated and avoid excessive sugar and processed foods. A healthy diet can help manage weight and improve thyroid health.
Monitoring Progress
Monitoring progress is crucial to understanding if weight gain is due to thyroid issues. Observing changes over time helps you identify patterns. This can inform more effective treatment plans.
Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential. They can monitor your thyroid function. Blood tests can detect changes in thyroid hormone levels. These tests include TSH, T3, and T4. A consistent schedule for check-ups ensures accurate tracking. Early detection of thyroid imbalances can prevent further complications.
| Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| TSH | Measures thyroid-stimulating hormone levels |
| T3 | Measures triiodothyronine levels |
| T4 | Measures thyroxine levels |
Symptom Tracking
Tracking symptoms helps you understand your thyroid health better. Common symptoms of thyroid issues include:
- Unexplained weight gain
- Fatigue
- Hair loss
- Dry skin
- Cold intolerance
Maintaining a symptom diary can be beneficial. Record the date, symptom, and intensity. This can help your doctor make an informed diagnosis. Consistency is key to accurate symptom tracking.
When To Seek Medical Advice
If weight gain persists, it might be a thyroid issue. This happens when the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough hormones, leading to various symptoms. Knowing when to seek medical advice can help manage and treat the condition effectively.
Persistent Symptoms
Thyroid-related weight gain often comes with other persistent symptoms. These include:
- Constant fatigue
- Dry skin
- Hair loss
- Cold intolerance
- Constipation
If these symptoms last more than a few weeks, it’s time to consult a doctor. Ignoring them may lead to worsening health issues.
Expert Consultation
An expert consultation can diagnose thyroid problems accurately. Doctors may perform blood tests to check hormone levels. This helps in identifying hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Here’s a simple table showing common tests and their purpose:
| Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| TSH Test | Measures Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone levels |
| T3 and T4 Tests | Measures actual thyroid hormone levels |
| Thyroid Antibody Tests | Detects autoimmune thyroid conditions |
Based on test results, doctors can prescribe appropriate treatments. These may include hormone replacement therapy, medications, or lifestyle changes.
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent serious complications. Don’t ignore persistent symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Thyroid-related Weight Gain Symptoms?
Unexplained weight gain, fatigue, and cold intolerance can be symptoms.
How Does Thyroid Affect Weight Gain?
Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism. Imbalance can lead to weight gain.
Can Hypothyroidism Cause Weight Gain?
Yes, hypothyroidism slows metabolism, causing weight gain.
What Tests Diagnose Thyroid-related Weight Gain?
Blood tests measuring TSH, T3, and T4 levels.
Are There Treatments For Thyroid-related Weight Gain?
Yes, medications like levothyroxine can help.
How Quickly Does Thyroid Treatment Affect Weight?
Improvements usually start within weeks, but weight loss may take longer.
Can Thyroid Issues Cause Sudden Weight Gain?
Yes, sudden weight gain can indicate thyroid problems.
Conclusion
Understanding if thyroid issues are causing weight gain is crucial for effective treatment. Regular check-ups and professional advice can help. Monitor symptoms and consult a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis. Early detection ensures better management of thyroid-related weight gain. Stay informed and proactive for your health.